The healthcare landscape stands at the precipice of a monumental transformation, driven by the relentless advancement of artificial intelligence (AI). Once confined to the realms of science fiction, AI is now a tangible force, rapidly integrating into every facet of medicine, from diagnostics and drug discovery to personalized treatment and patient care. This paradigm shift promises not just incremental improvements but revolutionary leaps in efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility, fundamentally redefining what’s possible in health and wellness. For healthcare professionals and tech enthusiasts alike, understanding the profound implications of this healthcare technology is crucial.
- The Dawn of a New Era: AI’s Current Footprint in Healthcare
- Diagnostics and Imaging: AI’s Precision in Early Detection
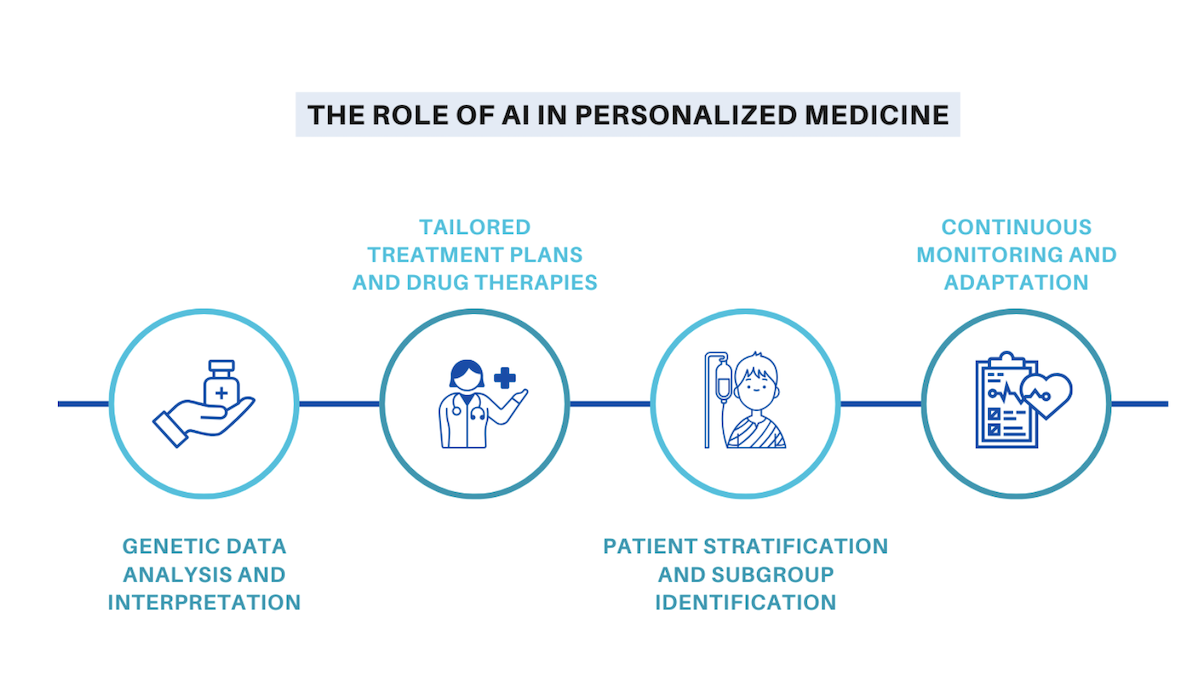
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailoring Therapies with AI
- Drug Discovery and Development: Accelerating Innovation
- Operational Efficiency and Administration: Streamlining Processes
- Unlocking Tomorrow: The Transformative Potential of AI in Healthcare
- Predictive Analytics for Proactive Care: Preventing Disease Before it Starts
- Robotics and Automation in Surgery and Rehabilitation: Enhanced Precision and Recovery
- Virtual Health Assistants and Remote Patient Monitoring: Expanding Access and Continuous Care
- Genomics and Precision Medicine: Revolutionizing Individualized Treatment
- Navigating the Labyrinth: Challenges and Ethical Considerations
The promise of artificial intelligence in healthcare is vast and multifaceted. It holds the potential to unlock new insights from complex data sets, automate routine tasks, and empower clinicians with unprecedented decision-making capabilities. We are moving towards an era where diseases are detected earlier, treatments are tailored with pinpoint precision, and medical innovations are accelerated at an astounding pace. This article will delve into the current applications of AI, explore its future potential, address the critical challenges and ethical considerations, and ultimately paint a picture of a symbiotic future where human expertise and artificial intelligence converge to deliver superior patient care. Prepare to journey into a future where technology doesn’t just assist healthcare, but fundamentally elevates it.
The Dawn of a New Era: AI’s Current Footprint in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence is no longer a distant dream; it’s actively reshaping the present state of medicine. Its current applications are diverse, demonstrating AI’s capacity to enhance various aspects of healthcare technology and improve outcomes for millions.

Diagnostics and Imaging: AI’s Precision in Early Detection
One of the most immediate and impactful applications of artificial intelligence is in medical diagnostics, particularly in interpreting complex imaging data. AI-powered algorithms can analyze X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and pathology slides with remarkable speed and accuracy, often surpassing human capabilities in identifying subtle anomalies. For instance, AI systems are proving highly effective in detecting early signs of cancer, retinal diseases, and neurological conditions, leading to earlier interventions and significantly better prognoses.
- Radiology Enhancement: AI tools assist radiologists by flagging suspicious areas, prioritizing urgent cases, and reducing the time spent on image analysis. This not only boosts efficiency but also minimizes diagnostic errors.
- Pathology Analysis: Machine learning models can analyze tissue biopsies to identify cancerous cells with high precision, aiding pathologists in grading tumors and predicting disease progression.
- Dermatology: AI-powered mobile applications can analyze skin lesions for signs of melanoma, offering preliminary assessments that can guide individuals to seek professional medical advice.
- Genomic Data Integration: AI can analyze vast amounts of genomic, proteomic, and clinical data to identify specific biomarkers that predict a patient’s response to certain drugs or therapies. This allows oncologists, for example, to select the most effective chemotherapy or immunotherapy for a cancer patient based on their tumor’s genetic signature.
- Drug Dosage Optimization: AI algorithms can monitor patient responses to medication, adjusting dosages in real-time to maximize efficacy and minimize side effects, particularly crucial in conditions requiring delicate balance, like diabetes or chronic pain management.
- Chronic Disease Management: AI-driven platforms can track vital signs, activity levels, and dietary intake for patients with chronic conditions, providing personalized recommendations and alerting healthcare providers to potential issues before they escalate.
- Target Identification: AI can sift through massive biological databases to identify novel drug targets and understand disease mechanisms at a molecular level.
- Molecule Synthesis and Screening: Machine learning models can predict the properties of millions of chemical compounds, identifying those most likely to bind to a specific target and exhibit therapeutic effects, significantly reducing the need for costly and time-consuming laboratory experiments.
- Clinical Trial Optimization: AI helps design more efficient clinical trials by identifying optimal patient cohorts, predicting trial outcomes, and monitoring patient safety, thereby reducing costs and bringing life-saving drugs to market faster.
- Appointment Scheduling and Management: AI-powered systems can manage complex scheduling, reduce no-show rates through intelligent reminders, and optimize resource allocation within clinics and hospitals.
- Medical Billing and Coding: Natural Language Processing (NLP) models can automate the arduous task of medical coding and billing, reducing errors and accelerating revenue cycles.
- Supply Chain Management: AI optimizes inventory management for hospitals and clinics, predicting demand for medical supplies and ensuring timely procurement, which is critical during public health crises.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms can analyze claims data to identify patterns indicative of fraud, saving healthcare systems billions of dollars annually.
- Population Health Management: AI can analyze public health data, environmental factors, and individual health records to identify populations at high risk for specific diseases, allowing for targeted preventative interventions.
- Early Warning Systems: For individuals, AI can monitor continuous biometric data from wearables and other devices, predicting the onset of conditions like sepsis, heart attacks, or diabetic crises hours or even days in advance, enabling timely medical intervention.
- Lifestyle Interventions: Personalized AI coaches can provide tailored recommendations for diet, exercise, and stress management based on an individual’s genetic predispositions and real-time health data, promoting long-term wellness.
- Autonomous Surgical Robots: While fully autonomous surgery is still in its nascent stages, AI-enhanced robotic systems already assist surgeons with intricate procedures, providing enhanced dexterity, tremor reduction, and real-time data overlays. Future developments could see increasingly autonomous tasks under human supervision, leading to even greater precision and efficiency.
- Exoskeletons and Prosthetics: AI-powered exoskeletons are transforming rehabilitation for patients with mobility impairments, assisting with movement and retraining muscles. Advanced AI-driven prosthetics offer more natural and intuitive control, significantly improving the quality of life for amputees.
- Drug Dispensing and Logistics: Robotic systems, guided by AI, can automate the dispensing of medications in hospitals and pharmacies, reducing human error and ensuring accurate delivery, especially crucial in complex hospital environments.
- AI-Powered Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: These intelligent interfaces can provide instant answers to common health questions, guide patients through symptom checkers, schedule appointments, and offer medication reminders. They can also act as a first point of contact, triaging patients to the appropriate level of care.
- Continuous Remote Monitoring: Wearable sensors and smart home devices, integrated with AI, will continuously collect vital health data (heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, sleep patterns). AI algorithms will analyze this data in real-time, identifying deviations from normal patterns and alerting healthcare providers to potential issues, allowing for proactive intervention, especially beneficial for the elderly or those with chronic conditions in rural areas.
- Telemedicine Enhancement: AI can enrich telemedicine consultations by providing clinicians with comprehensive patient data summaries, predictive insights, and even real-time language translation for diverse patient populations.
- Unlocking Genomic Secrets: AI can analyze vast genomic datasets, identifying complex interactions between genes, environment, and disease. This helps in understanding disease etiology, identifying genetic predispositions, and discovering novel therapeutic targets.
- Predicting Drug Response: By correlating an individual’s genetic profile with drug efficacy and side effect data, AI can predict how a patient will respond to specific medications, guiding clinicians to select the most effective and safest treatment options.
- CRISPR and Gene Editing Optimization: AI is being used to optimize gene-editing techniques like CRISPR, identifying ideal target sites and predicting off-target effects, making these revolutionary medical innovations safer and more precise.
- HIPAA Compliance and Beyond: Adhering to strict regulatory frameworks like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is essential, but AI systems often require data from diverse sources, necessitating even more robust security protocols and anonymization techniques.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Healthcare data is a prime target for cyberattacks. AI systems, if not properly secured, could become new vulnerabilities, exposing highly personal medical information.
- Consent and Data Ownership: Clear guidelines are needed regarding how patient data is collected, stored, used, and shared, ensuring individuals retain control over their health information.
- Underrepresentation in Datasets: If training data disproportionately represents certain demographics (e.g., primarily white males), AI models may perform poorly or incorrectly for underrepresented groups (e.g., women, ethnic minorities), leading to misdiagnosis or ineffective treatments.
- Exacerbating Health Disparities: Biased AI could worsen existing health disparities, for instance, by recommending less aggressive treatments for certain populations or misinterpreting symptoms based on racial or socioeconomic factors.
- Auditing and Transparency: Robust mechanisms are needed to audit AI algorithms for bias, ensure transparency in their decision-making processes, and actively work to diversify training datasets.
- Lack of Clear Frameworks: The absence of comprehensive regulatory frameworks for AI in medicine makes it challenging for innovators to navigate the approval process and for healthcare providers to understand their legal responsibilities.
- Physician Acceptance and Training: Healthcare professionals, while often keen on medical innovations, may be hesitant to adopt AI tools due to a lack of understanding, concerns about job displacement, or insufficient training.
- Interoperability and Integration: Integrating new AI systems with existing, often legacy, healthcare IT infrastructure can be complex and costly, hindering widespread adoption.
- Loss of Human Connection: Over-reliance on AI could lead to a depersonalization of healthcare, diminishing the crucial human-to-human interaction that builds trust and provides emotional support.
- Ethical Decision-Making: AI can provide probabilities and recommendations, but complex ethical dilemmas in medicine often require human judgment, moral reasoning, and an understanding of individual values.
- Accountability: Establishing clear lines of accountability when AI is involved in critical medical decisions is essential. Who is responsible if an AI makes an error that harms a patient?
This precision in early detection, driven by advanced healthcare technology, is a cornerstone of proactive patient care.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailoring Therapies with AI
The concept of “one-size-fits-all” medicine is rapidly becoming obsolete. Artificial intelligence is at the forefront of ushering in an era of truly personalized medicine, where treatment regimens are meticulously tailored to an individual’s unique biological makeup, lifestyle, and disease profile.
These medical innovations are transforming the delivery of patient care, making it more effective and less burdensome.

Drug Discovery and Development: Accelerating Innovation
The journey from a promising molecule to an approved drug is notoriously long, expensive, and fraught with failures. Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing this process, dramatically accelerating drug discovery and development by identifying potential drug candidates, predicting their efficacy and toxicity, and optimizing clinical trial designs.
This application of healthcare technology is a game-changer, fostering unprecedented medical innovations that benefit global health.

Operational Efficiency and Administration: Streamlining Processes
Beyond direct patient interaction, artificial intelligence is also making significant inroads into optimizing the administrative and operational aspects of healthcare. This includes automating routine tasks, improving resource allocation, and enhancing overall system efficiency, freeing up human staff to focus on more complex patient care needs.
By streamlining these processes, artificial intelligence contributes indirectly but significantly to better patient care by making healthcare systems more robust and responsive.
Unlocking Tomorrow: The Transformative Potential of AI in Healthcare
While current applications are impressive, the true power of artificial intelligence in healthcare is yet to be fully realized. The future promises even more profound transformations, pushing the boundaries of medical innovations and redefining the very essence of patient care.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Care: Preventing Disease Before it Starts
Imagine a healthcare system that doesn’t just react to illness but actively predicts and prevents it. This is the promise of AI-driven predictive analytics, a cornerstone of future healthcare technology.
This proactive approach, powered by artificial intelligence, shifts the focus from treatment to prevention, leading to healthier communities and reduced healthcare burdens.
Robotics and Automation in Surgery and Rehabilitation: Enhanced Precision and Recovery
Robotics, often intertwined with artificial intelligence, is set to revolutionize surgical procedures and rehabilitation therapies, offering unparalleled precision, minimally invasive options, and improved recovery outcomes.
These medical innovations highlight the tangible benefits of integrating healthcare technology with human expertise for superior patient care.
Virtual Health Assistants and Remote Patient Monitoring: Expanding Access and Continuous Care
The future of patient care will be characterized by greater accessibility and continuous monitoring, thanks to artificial intelligence powering virtual health assistants and advanced remote monitoring solutions.
This expansion of healthcare technology ensures that quality patient care is not limited by geography or time, making healthcare more inclusive and responsive.
Genomics and Precision Medicine: Revolutionizing Individualized Treatment
The convergence of artificial intelligence and genomics is unlocking unprecedented potential for truly individualized medicine, moving beyond generalized treatments to therapies precisely engineered for each patient.
This deep dive into an individual’s genetic blueprint, facilitated by artificial intelligence, promises to revolutionize patient care by making treatments exquisitely tailored and maximally effective.
Navigating the Labyrinth: Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the potential of artificial intelligence in healthcare is immense, its widespread adoption and ethical integration are not without significant challenges. Addressing these hurdles is paramount to ensuring that healthcare technology serves humanity equitably and responsibly.
Data Privacy and Security: Protecting Sensitive Information
The very foundation of AI in healthcare relies on access to vast amounts of sensitive patient data. This raises critical concerns regarding privacy, security, and the potential for misuse.
The ethical deployment of artificial intelligence hinges on unwavering commitment to data protection, safeguarding the trust essential for effective patient care.
Bias in AI Algorithms: Ensuring Equitable Care
AI algorithms learn from the data they are trained on. If this data is biased – reflecting historical inequities, underrepresentation of certain demographic groups, or systemic prejudices – the AI will perpetuate and even amplify those biases, leading to unequal or suboptimal patient care.
Addressing algorithmic bias is not merely a technical challenge; it’s an ethical imperative for medical innovations to truly serve all.
Regulatory Hurdles and Adoption Barriers: Overcoming Resistance
The rapid pace of artificial intelligence development often outstrips the ability of regulatory bodies to keep up, creating an environment of uncertainty for both developers and users of healthcare technology.
Overcoming these barriers requires collaborative efforts between policymakers, industry leaders, and healthcare practitioners to foster an environment conducive to responsible healthcare technology adoption.
The Human Element: Maintaining Empathy and Trust
While artificial intelligence excels at data analysis and automation, it cannot replicate the uniquely human qualities of empathy, compassion, and intuition that are vital to patient care.
The future of artificial intelligence in healthcare must prioritize augmenting