- Decoding the Smart Home Landscape: Convenience Meets Vulnerability
- Unmasking Common Cyber Threats to Your Smart Home Devices
- Unauthorized Access and Device Hijacking
- Data Breaches and Privacy Invasion
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
- Malware and Ransomware Infiltration
- Physical Security Exploits
- Foundational Strategies for Robust Smart Home Security
- 1. Fortify Your Wi-Fi Network: The First Line of Defense
- 2. Banish Default Passwords: A Critical Oversight
- 3. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Everywhere Possible
- 4. Keep Devices Updated: Patching Vulnerabilities
- 5. Review Device Permissions and Privacy Settings
- 6. Implement Network Segmentation (VLANs)
- Advanced Privacy Protection and Vigilance in Your Smart Home
- 1. Consider a Dedicated Smart Home Hub
- 2. Deploy a Robust Firewall
- 3. Monitor Network Traffic for Anomalies
- 4. Be Wary of Voice Assistants and Cameras
- 5. Secure Discarded Devices
- 6. Understand and Manage Data Collection Policies
- The Human Element: User Awareness and Vigilance
- Responding to a Smart Home Security Breach: What to Do
- Frequently Asked Questions About Smart Home Security
Fortify Your Digital Fortress: Essential Smart Home Security Against Cyber Threats
The allure of a smart home is undeniable. Imagine lights that dim automatically, thermostats that learn your preferences, and security cameras you can monitor from anywhere. This convenience, however, comes with a significant caveat: every connected device is a potential doorway for cyber threats. As our homes become increasingly intertwined with the Internet of Things (IoT), the urgency to implement robust smart home security measures has never been greater. Without proper safeguards, your smart devices, designed to simplify life, can become vulnerabilities, exposing your personal data and digital privacy to malicious actors.
This comprehensive guide is designed for homeowners and tech-savvy individuals who recognize the critical need to protect their digital sanctuaries. We’ll delve into the specific cyber threats targeting your connected ecosystem and equip you with practical, actionable strategies to secure your internet of things devices. From fundamental network hardening to advanced privacy protection techniques, you’ll learn how to transform your smart home from a potential target into a fortified digital fortress. Don’t wait until a breach occurs; understanding and implementing these security protocols now is an imperative step towards safeguarding your family’s digital well-being.
Decoding the Smart Home Landscape: Convenience Meets Vulnerability
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized how we live, work, and interact with our environments. Smart home devices—from smart speakers and security cameras to smart thermostats and door locks—offer unparalleled convenience and efficiency. These devices connect to your home network and, often, to the internet, allowing remote control, automation, and data exchange. While these capabilities enhance our daily lives, they also introduce a complex web of potential entry points for those with malicious intent.
Every smart device, regardless of its function, represents a node in your home’s digital infrastructure. Each node can be exploited if not properly secured, making comprehensive smart home security a critical concern. The sheer volume and diversity of these devices make securing them a unique challenge, often overlooked by manufacturers who prioritize functionality and ease of use over stringent security protocols. This creates an urgent need for homeowners to take proactive steps in protecting their digital domains.

Unmasking Common Cyber Threats to Your Smart Home Devices
Understanding the enemy is the first step in effective defense. Cyber threats targeting smart homes are diverse and constantly evolving, ranging from simple unauthorized access to sophisticated data breaches. Recognizing these common vulnerabilities is crucial for developing a robust privacy protection strategy.
Unauthorized Access and Device Hijacking
One of the most immediate dangers is unauthorized access. If an attacker gains control of a single smart device—say, a security camera or a smart lock—they could compromise your physical security or surveil your home. Weak passwords, unpatched firmware, or default credentials are prime targets for hackers looking to hijack devices. Imagine your smart thermostat being manipulated to waste energy, or worse, your smart garage door opening unexpectedly.

Data Breaches and Privacy Invasion
Many smart home devices collect vast amounts of personal data, including usage patterns, voice commands, video feeds, and even biometric information. If these devices or the cloud services they connect to are breached, this sensitive data can be stolen. This poses a severe risk to your privacy protection, potentially leading to identity theft, blackmail, or targeted advertising based on highly personal information. Data breaches are not just about financial loss; they are about the erosion of your personal space and autonomy.
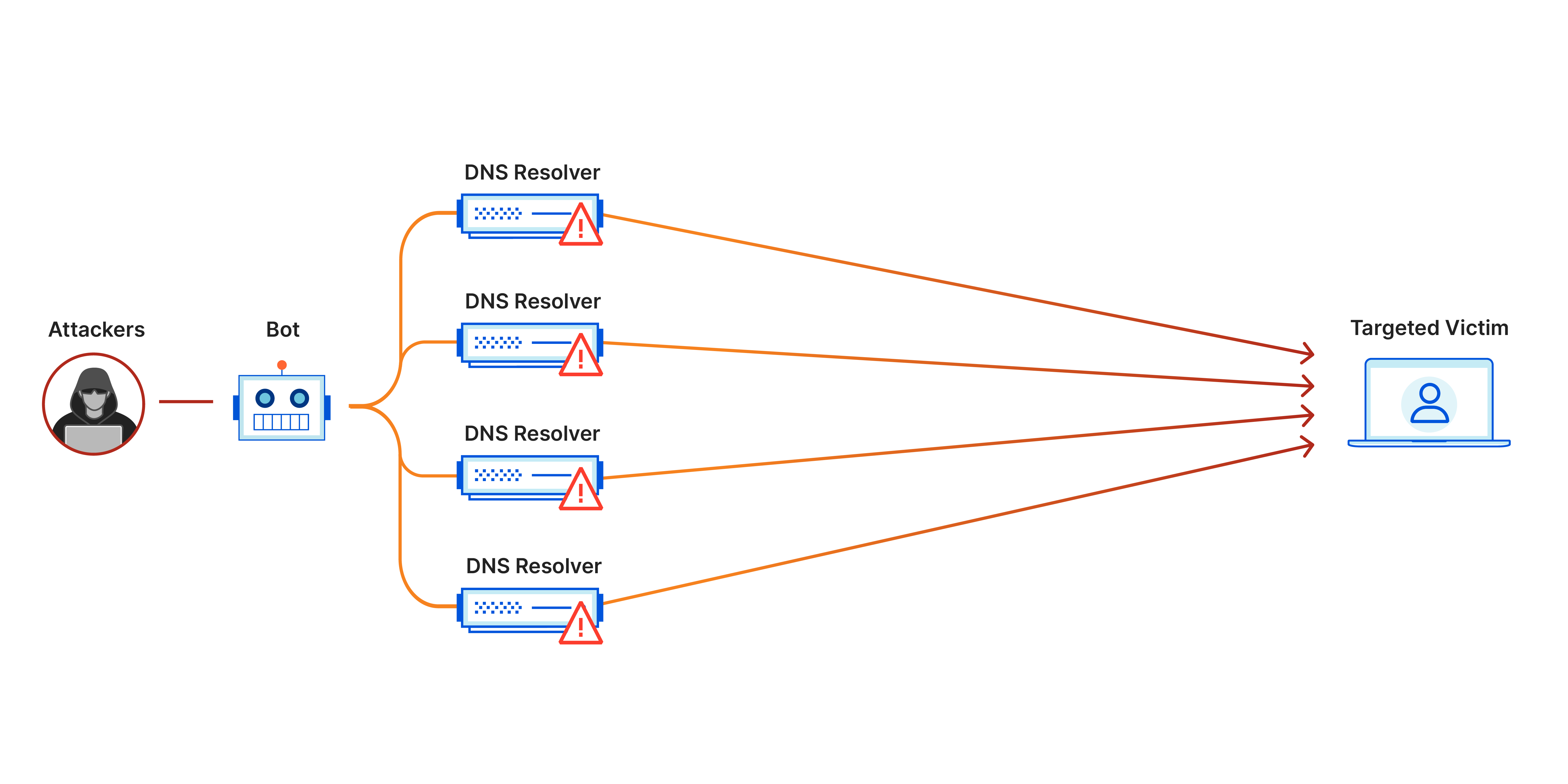
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
While less common for individual smart homes, a compromised IoT device can be conscripted into a botnet, a network of hijacked devices used to launch DDoS attacks against larger targets. This means your smart kettle could inadvertently be part of an attack that takes down a major website. While it might not directly harm you, it contributes to a larger cybercrime ecosystem and can slow down your own internet connection.
Malware and Ransomware Infiltration
Just like computers, smart devices can be infected with malware. This malicious software can allow attackers to spy on you, steal data, or even lock you out of your devices until a ransom is paid. Ransomware, in particular, can render your smart home unusable, demanding payment to restore functionality. The interconnected nature of smart homes means that malware on one device could potentially spread to others on your network.
Physical Security Exploits
Sometimes, the threat isn’t purely digital. Devices that control physical access, like smart locks or garage door openers, can be vulnerable to exploits that grant unauthorized entry to your home. This could involve manipulating the device’s software, intercepting signals, or even exploiting physical design flaws. The integration of the digital with the physical makes these threats particularly alarming.
Foundational Strategies for Robust Smart Home Security
Securing your internet of things devices requires a multi-layered approach, starting with the very foundation of your home network. These essential steps are non-negotiable for anyone serious about smart home security and privacy protection.
1. Fortify Your Wi-Fi Network: The First Line of Defense
Your Wi-Fi network is the gateway to your smart home. Securing it is paramount.
- Strong, Unique Passwords: Change the default password of your router immediately. Use a complex password (at least 12-16 characters) combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid easily guessable information.
- WPA3 Encryption: Ensure your router uses WPA3 encryption, the latest and most secure Wi-Fi security protocol. If WPA3 isn’t available, use WPA2-AES. Avoid WEP or WPA/WPA2-TKIP, which are easily cracked.
- Rename Your Network: Change the default SSID (network name) to something generic that doesn’t reveal personal information about your location or internet service provider.
- Disable WPS: Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is convenient but has known security vulnerabilities. Disable it in your router settings.
- Guest Network: Set up a separate guest Wi-Fi network for visitors and, ideally, for your less critical smart devices. This segregates them from your main network, limiting potential damage if a guest device or a smart device is compromised.
- Change Every Default Password: For every single smart device you bring into your home—cameras, doorbells, hubs, light bulbs—immediately change its default credentials to strong, unique passwords. Use a password manager to keep track of them all.
- Why it’s Urgent: Default passwords are the easiest entry point for attackers, allowing them to instantly gain control of your devices.
- Mandatory for Critical Devices: Enable 2FA for your smart home hub, security cameras, smart locks, and any accounts linked to these devices (e.g., Amazon, Google, Apple).
- Enhanced Protection: Even if your password is stolen, an attacker cannot access your account without the second factor.
- Enable Automatic Updates: Where available, enable automatic firmware and software updates for all your smart devices and your router.
- Manual Checks: For devices without automatic updates, regularly check the manufacturer’s website for new firmware versions and install them promptly.
- The Urgency of Patches: Hackers actively exploit known vulnerabilities, so keeping your devices current is a race against time.
- Read Privacy Policies: Before purchasing or setting up a device, read its privacy policy to understand its data collection practices.
- Limit Permissions: Only grant necessary permissions. For example, a smart light bulb probably doesn’t need access to your location data.
- Disable Unused Features: If a device has features you don’t use (e.g., a microphone on a device where you only need video), disable them to reduce potential attack surfaces.
- Isolate IoT Devices: Create a separate VLAN for your IoT devices, isolating them from your main network where your computers, smartphones, and sensitive data reside.
- Contain Breaches: If an IoT device on the segmented network is compromised, the attacker’s access is restricted to that VLAN, preventing them from reaching your more critical devices.
- Centralized Control: Hubs like Samsung SmartThings, Hubitat, or Home Assistant can manage local communication between devices, reducing their direct exposure to the internet.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Some hubs offer better security features and can isolate devices, making it harder for external threats to reach individual components.
- Next-Generation Firewalls: Consider a dedicated firewall appliance or a router with advanced firewall capabilities to monitor and filter incoming and outgoing traffic more rigorously.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Some advanced network devices include IDS/IPS features that can detect and prevent malicious activity in real-time.
- Network Monitoring Tools: Tools like Wireshark or even features built into some routers can help you observe unusual data transfers or connections from your smart devices.
- Unusual Activity: Look for devices communicating with unknown external IP addresses or sending large amounts of data unexpectedly.
- Strategic Placement: Position smart cameras carefully, avoiding areas where they might capture highly private moments. Consider disabling them when not needed.
- Microphone Control: Many smart speakers have a physical mute button for the microphone. Use it when you don’t need the device actively listening.
- Data Retention: Regularly review and delete voice recordings and video footage stored by cloud-connected devices, if the option is available.
- Factory Reset: Perform a factory reset on any device before selling, donating, or discarding it.
- Data Erasure: For devices with internal storage, follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure data is completely erased, not just deleted.
- Opt-Out of Data Sharing: Where possible, opt out of data sharing programs or personalized advertising features.
- Review Settings Regularly: Periodically revisit the privacy settings of your smart devices and associated apps as manufacturers often introduce new features or change policies.
- Phishing Awareness: Be extremely cautious of suspicious emails, texts, or calls claiming to be from your smart device manufacturer or service provider. Always verify the source before clicking links or providing credentials.
- Strong Password Hygiene: Never reuse passwords across different accounts, especially for critical services.
- Physical Security: Don’t forget the basics. Ensure physical access to your router and smart home hub is restricted.
- Educate Family Members: Ensure everyone in your household understands the importance of strong passwords, updates, and cautious online behavior.
- Isolate the Device: If you suspect a specific device is compromised, disconnect it from your network immediately.
- Change Passwords: Change all passwords associated with the compromised device and any linked accounts.
- Run Security Scans: If you suspect malware, run security scans on your network and connected computers.
- Notify Manufacturer: Report the issue to the device manufacturer. They may have specific guidance or a patch.
- Review Network Logs: Check your router’s logs for any unusual activity.
- Consider a Factory Reset: As a last resort, perform a factory reset on the compromised device, but only after changing passwords and understanding the implications.
2. Banish Default Passwords: A Critical Oversight
This is perhaps the most overlooked yet critical step. Every smart device often comes with a default username and password (e.g., “admin/admin,” “user/password”). Hackers know these defaults and actively scan for devices using them.
3. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Everywhere Possible
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method (like a code from your phone or a fingerprint) in addition to your password.
4. Keep Devices Updated: Patching Vulnerabilities
Software and firmware updates often include critical security patches that fix newly discovered vulnerabilities. Neglecting updates leaves your devices exposed.
5. Review Device Permissions and Privacy Settings
Many smart devices request extensive permissions during setup. It’s crucial to understand what data they collect and how it’s used.
6. Implement Network Segmentation (VLANs)
For tech-savvy individuals, network segmentation using Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) can significantly enhance smart home security.
Advanced Privacy Protection and Vigilance in Your Smart Home
Beyond the foundational steps, adopting advanced strategies and maintaining constant vigilance are crucial for comprehensive privacy protection in your connected home.
1. Consider a Dedicated Smart Home Hub
Instead of having every device connect directly to your Wi-Fi router and the internet, a dedicated smart home hub can centralize control and potentially enhance security.
2. Deploy a Robust Firewall
While your router has a basic firewall, a more advanced firewall solution can provide deeper packet inspection and control over network traffic.
3. Monitor Network Traffic for Anomalies
Being aware of what’s happening on your network can help you spot potential cyber threats early.
4. Be Wary of Voice Assistants and Cameras
These devices, while convenient, are often at the forefront of privacy protection concerns.
5. Secure Discarded Devices
When you upgrade or dispose of smart devices, ensure they are properly wiped of all personal data.
6. Understand and Manage Data Collection Policies
Many smart devices collect data to improve services, but this data can also be a privacy risk.
The Human Element: User Awareness and Vigilance
No matter how sophisticated your technological defenses, the human element remains the weakest link in smart home security. Your habits and awareness are just as important as the devices themselves.
Responding to a Smart Home Security Breach: What to Do
Even with the best precautions, a breach can sometimes occur. Knowing how to react quickly is crucial.





